0040001 /*0040002 ip_lib.c0040003 0040004 Copyright 1995 Philip Homburg0040005 */ip_lib.c contains functions that deal with subnet masks and a function that verifies ip options.
0040006 0040007 #include "inet.h"0040008 #include "buf.h"0040009 #include "event.h"0040010 #include "type.h"0040011 0040012 #include "assert.h"0040013 #include "io.h"0040014 #include "ip_int.h"0040015 0040016 THIS_FILE0040017 0040018 PUBLIC ipaddr_t ip_get_netmask (hostaddr)0040019 ipaddr_t hostaddr;ip_get_netmask()
ip_get_netmask(hostaddr) simply returns the natural subnet mask of hostaddr, the only parameter to ip_get_netmask().
For a class A network, the subnet mask is 255.000.000.000 (0xff000000);
for a class B network, the subnet mask is 255.255.000.000 (0xffff0000);
for a class C network, the subnet mask is 255.255.255.000 (0xffffff00);
for a zero network type (0.xx.xx.xx), the subnet mask is (0x00000000).
ip_get_netmask(hostaddr) simply returns the natural subnet mask of hostaddr, the only parameter to ip_get_netmask().
For a class A network, the subnet mask is 255.000.000.000 (0xff000000);
for a class B network, the subnet mask is 255.255.000.000 (0xffff0000);
for a class C network, the subnet mask is 255.255.255.000 (0xffffff00);
for a zero network type (0.xx.xx.xx), the subnet mask is (0x00000000).
0040020 {0040021 return ip_netmask(ip_nettype(hostaddr));ip_netmask()
ip_netmask() returns a nettype's associated subnet mask.
For a class A network, the subnet mask is 255.000.000.000 (0xff000000);
for a class B network, the subnet mask is 255.255.000.000 (0xffff0000);
for a class C network, the subnet mask is 255.255.255.000 (0xffffff00);
for a zero network type (0.xx.xx.xx), the subnet mask is (0x00000000).
Note that the returned subnet mask is in network format.ip_nettype()
ip_nettype(ipaddr) returns the network type (which will be of type nettype_t) of ipaddr, the only parameter to ip_nettype().
The nettype_t enum typedef is declared in inet/generic/ip_int.h. Each type's associated ip address range is included in the comments.
ip_netmask() returns a nettype's associated subnet mask.
For a class A network, the subnet mask is 255.000.000.000 (0xff000000);
for a class B network, the subnet mask is 255.255.000.000 (0xffff0000);
for a class C network, the subnet mask is 255.255.255.000 (0xffffff00);
for a zero network type (0.xx.xx.xx), the subnet mask is (0x00000000).
Note that the returned subnet mask is in network format.ip_nettype()
ip_nettype(ipaddr) returns the network type (which will be of type nettype_t) of ipaddr, the only parameter to ip_nettype().
The nettype_t enum typedef is declared in inet/generic/ip_int.h. Each type's associated ip address range is included in the comments.
typedef enum nettype
{
IPNT_ZERO, /* 0.xx.xx.xx */
IPNT_CLASS_A, /* 1.xx.xx.xx .. 126.xx.xx.xx */
IPNT_LOCAL, /* 127.xx.xx.xx */
IPNT_CLASS_B, /* 128.xx.xx.xx .. 191.xx.xx.xx */
IPNT_CLASS_C, /* 192.xx.xx.xx .. 223.xx.xx.xx */
IPNT_CLASS_D, /* 224.xx.xx.xx .. 239.xx.xx.xx */
IPNT_CLASS_E, /* 240.xx.xx.xx .. 247.xx.xx.xx */
IPNT_MARTIAN, /* 248.xx.xx.xx .. 254.xx.xx.xx + */
IPNT_BROADCAST /* 255.255.255.255 */
} nettype_t;
0040022 }0040023 0040024 PUBLIC int ip_chk_hdropt (opt, optlen)0040025 u8_t *opt;0040026 int optlen;ip options
Ip options are an assortment of settings related to the ip protocol. However, most ip options involve the path that the ip packet takes to its destination. Ip options are discussed in detail on page 14 of RFC 791 as well as by the Data Network Resource.
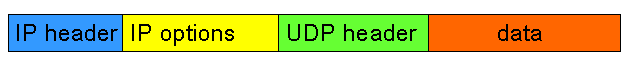
Ip options are optional. If there are ip options, the ip options must be placed between the ip header and the udp header (for a udp packet):
The maximum size of the ip options is 40 bytes and must be a multiple of 4 bytes (RFC 791). This is a real limitation since the number of router ip addresses that can be stored in the ip options is very limited. ip_chk_hdropt()
ip_chk_hdropt() goes through the ip header options (if there are any) and verifies that the options are acceptable. For example, ip_chk_hdropt() verifies that the same ip header option is not listed twice.
Ip options are an assortment of settings related to the ip protocol. However, most ip options involve the path that the ip packet takes to its destination. Ip options are discussed in detail on page 14 of RFC 791 as well as by the Data Network Resource.
Ip options are optional. If there are ip options, the ip options must be placed between the ip header and the udp header (for a udp packet):

The maximum size of the ip options is 40 bytes and must be a multiple of 4 bytes (RFC 791). This is a real limitation since the number of router ip addresses that can be stored in the ip options is very limited. ip_chk_hdropt()
ip_chk_hdropt() goes through the ip header options (if there are any) and verifies that the options are acceptable. For example, ip_chk_hdropt() verifies that the same ip header option is not listed twice.
0040027 {0040028 int i, security_present= FALSE, lose_source_present= FALSE,0040029 strict_source_present= FALSE, record_route_present= FALSE,0040030 timestamp_present= FALSE;The variables security_present, lose_source_present, etc. are used to make sure that an option is not used more than once. After encountering one of these options, ip_chk_hdropt() sets the corresponding variable to true (e.g., line 40049).
0040031 0040032 assert (!(optlen & 3));0040033 i= 0;0040034 while (i<optlen)0040035 {0040036 DBLOCK(1, printf("*opt= %d\n", *opt));0040037 0040038 switch (*opt)0040039 {0040040 case 0x0: /* End of Option list */0040041 return NW_OK;0040042 case 0x1: /* No Operation */An option of 0x01 is a no-op (no operation). A no-op is used to internally pad options within the options header field (recall that the length of the ip options must be a multiple of 4).
0040043 i++;0040044 opt++;0040045 break;0040046 case 0x82: /* Security */Security options are used to specify military security flags and are used only in military networks.
0040047 if (security_present)0040048 return EINVAL;0040049 security_present= TRUE;0040050 if (opt[1] != 11)0040051 return EINVAL;0040052 i += opt[1];0040053 opt += opt[1];0040054 break;0040055 case 0x83: /* Lose Source and Record Route */Loose source routing suggests a network path that the ip packet take. Variations are allowed as long as all of the routers that are listed (actually, their ip addresses are listed) are in the packet's path.
Record route indicates that routers should record their ip addresses. This allows the destination to see the route that the packet took.
Record route indicates that routers should record their ip addresses. This allows the destination to see the route that the packet took.
0040056 if (lose_source_present)0040057 {0040058 DBLOCK(1, printf("snd lose soruce route\n"));0040059 return EINVAL;0040060 }0040061 lose_source_present= TRUE;0040062 if (opt[1]<3)0040063 {0040064 DBLOCK(1,0040065 printf("wrong length in source route\n"));0040066 return EINVAL;0040067 }0040068 i += opt[1];0040069 opt += opt[1];0040070 break;0040071 case 0x89: /* Strict Source and Record Route */Strict source routing identifies the path that an ip packet must take.
Record route indicates that routers should record their ip addresses. This allows the destination to see the route that the packet took. It's unclear why the route should be recorded for strict source routing since the source mandates the path for strict source routing.
Record route indicates that routers should record their ip addresses. This allows the destination to see the route that the packet took. It's unclear why the route should be recorded for strict source routing since the source mandates the path for strict source routing.
0040072 if (strict_source_present)0040073 return EINVAL;0040074 strict_source_present= TRUE;0040075 if (opt[1]<3)0040076 return EINVAL;0040077 i += opt[1];0040078 opt += opt[1];0040079 break;0040080 case 0x7: /* Record Route */Record route indicates that routers should record their ip addresses. This allows the destination to see the route that the packet took.
0040081 if (record_route_present)0040082 return EINVAL;0040083 record_route_present= TRUE;0040084 if (opt[1]<3)0040085 return EINVAL;0040086 i += opt[1];0040087 opt += opt[1];0040088 break;0040089 case 0x88:0040090 if (timestamp_present)0040091 return EINVAL;0040092 timestamp_present= TRUE;0040093 if (opt[1] != 4)0040094 return EINVAL;0040095 switch (opt[3] & 0xff)0040096 {0040097 case 0:0040098 case 1:0040099 case 3:0040100 break;0040101 default:0040102 return EINVAL;0040103 }0040104 i += opt[1];0040105 opt += opt[1];0040106 break;0040107 default:0040108 return EINVAL;0040109 }0040110 }0040111 if (i > optlen)0040112 {0040113 DBLOCK(1, printf("option of wrong length\n"));0040114 return EINVAL;0040115 }0040116 return NW_OK;0040117 }0040118 0040119 PUBLIC void ip_print_frags(acc)0040120 acc_t *acc;0040121 {0040122 #if DEBUG0040123 ip_hdr_t *ip_hdr;0040124 int first;0040125 0040126 if (!acc)0040127 printf("(null)");0040128 0040129 for (first= 1; acc; acc= acc->acc_ext_link, first= 0)0040130 {0040131 assert (acc->acc_length >= IP_MIN_HDR_SIZE);0040132 ip_hdr= (ip_hdr_t *)ptr2acc_data(acc);0040133 if (first)0040134 {0040135 writeIpAddr(ip_hdr->ih_src);0040136 printf(" > ");0040137 writeIpAddr(ip_hdr->ih_dst);0040138 }0040139 printf(" {%x:%d@%d%c}", ntohs(ip_hdr->ih_id),0040140 ntohs(ip_hdr->ih_length), 0040141 (ntohs(ip_hdr->ih_flags_fragoff) & IH_FRAGOFF_MASK)*8,0040142 (ntohs(ip_hdr->ih_flags_fragoff) & IH_MORE_FRAGS) ?0040143 '+' : '\0');0040144 }0040145 #endif0040146 }0040147 0040148 PUBLIC ipaddr_t ip_get_ifaddr(port_nr)ip_get_ifaddr()
ip_get_ifaddr(port_nr) simply returns the ip address of the ip port whose index within ip_port_table[] is port_nr, ip_get_ifaddr()'s only parameter.
ip_get_ifaddr(port_nr) simply returns the ip address of the ip port whose index within ip_port_table[] is port_nr, ip_get_ifaddr()'s only parameter.
0040149 int port_nr;0040150 {0040151 assert(port_nr >= 0 && port_nr < ip_conf_nr);0040152 0040153 return ip_port_table[port_nr].ip_ipaddr;0040154 }0040155 0040156 PUBLIC nettype_t ip_nettype(ipaddr)0040157 ipaddr_t ipaddr;ip_nettype()
ip_nettype(ipaddr) returns the network type (which will be of type nettype_t) of ipaddr, the only parameter to ip_nettype().
The nettype_t enum typedef is declared in inet/generic/ip_int.h. Each type's associated ip address range is included in the comments.
ip_nettype(ipaddr) returns the network type (which will be of type nettype_t) of ipaddr, the only parameter to ip_nettype().
The nettype_t enum typedef is declared in inet/generic/ip_int.h. Each type's associated ip address range is included in the comments.
typedef enum nettype
{
IPNT_ZERO, /* 0.xx.xx.xx */
IPNT_CLASS_A, /* 1.xx.xx.xx .. 126.xx.xx.xx */
IPNT_LOCAL, /* 127.xx.xx.xx */
IPNT_CLASS_B, /* 128.xx.xx.xx .. 191.xx.xx.xx */
IPNT_CLASS_C, /* 192.xx.xx.xx .. 223.xx.xx.xx */
IPNT_CLASS_D, /* 224.xx.xx.xx .. 239.xx.xx.xx */
IPNT_CLASS_E, /* 240.xx.xx.xx .. 247.xx.xx.xx */
IPNT_MARTIAN, /* 248.xx.xx.xx .. 254.xx.xx.xx + */
IPNT_BROADCAST /* 255.255.255.255 */
} nettype_t;
0040158 {0040159 u8_t highbyte;0040160 nettype_t nettype;0040161 0040162 ipaddr= ntohl(ipaddr);htons() / ntohs() / htonl() / ntohl()
From htons(3):
"htons() converts a 16-bit quantity from host byte order to network byte order."
Different CPU architectures group multiple bytes differently. For example, on a "little-endian" machine (an example of which is the Intel CPU), the value 0x1234 is stored in memory as 0x3412. However, on a "big-endian" machine, the value 0x1234 is stored in memory as 0x1234.
It is important that values in a header are sent across a network in a consistent manner independent of the architecture of the sending or receiving system. For this reason, a standard was chosen. The standard chosen was big-endian although it could have just as well been little-endian.
htons() is defined in /include/net/hton.h, as:
#define htons(x) (_tmp=(x), ((_tmp>>8) & 0xff) | ((_tmp<<8) & 0xff00))
ntohs() converts a 16-bit quantity from network byte order to host byte order, the reverse of htons().
htonl() and ntohl() are identical to htons() and ntohs() except that they convert 32-bit quantities instead of 16-bit quantities.
Processes generally supply header information when sending packets. The data in these fields is converted to the network format (i.e., big-endian) by the process before the process copies the data to the network service.
From htons(3):
"htons() converts a 16-bit quantity from host byte order to network byte order."
Different CPU architectures group multiple bytes differently. For example, on a "little-endian" machine (an example of which is the Intel CPU), the value 0x1234 is stored in memory as 0x3412. However, on a "big-endian" machine, the value 0x1234 is stored in memory as 0x1234.
It is important that values in a header are sent across a network in a consistent manner independent of the architecture of the sending or receiving system. For this reason, a standard was chosen. The standard chosen was big-endian although it could have just as well been little-endian.
htons() is defined in /include/net/hton.h, as:
#define htons(x) (_tmp=(x), ((_tmp>>8) & 0xff) | ((_tmp<<8) & 0xff00))
ntohs() converts a 16-bit quantity from network byte order to host byte order, the reverse of htons().
htonl() and ntohl() are identical to htons() and ntohs() except that they convert 32-bit quantities instead of 16-bit quantities.
Processes generally supply header information when sending packets. The data in these fields is converted to the network format (i.e., big-endian) by the process before the process copies the data to the network service.
0040163 highbyte= (ipaddr >> 24) & 0xff;0040164 if (highbyte == 0)0040165 {0040166 if (ipaddr == 0)0040167 nettype= IPNT_ZERO;0040168 else0040169 nettype= IPNT_MARTIAN;0040170 }0040171 else if (highbyte < 127)0040172 nettype= IPNT_CLASS_A;0040173 else if (highbyte == 127)0040174 nettype= IPNT_LOCAL;0040175 else if (highbyte < 192)0040176 nettype= IPNT_CLASS_B;0040177 else if (highbyte < 224)0040178 nettype= IPNT_CLASS_C;0040179 else if (highbyte < 240)0040180 nettype= IPNT_CLASS_D;0040181 else if (highbyte < 248)0040182 nettype= IPNT_CLASS_E;0040183 else if (highbyte < 255)0040184 nettype= IPNT_MARTIAN;0040185 else0040186 {0040187 if (ipaddr == (ipaddr_t)-1)Casting -1 to the ipaddr_t type results to 0xffffffff (255.255.255.255), the broadcast address.
The ipaddr_t typedef is declared in include/net/gen/in.h:
typedef u32_t ipaddr_t;
The ipaddr_t typedef is declared in include/net/gen/in.h:
typedef u32_t ipaddr_t;
0040188 nettype= IPNT_BROADCAST;0040189 else0040190 nettype= IPNT_MARTIAN;0040191 }0040192 return nettype;0040193 }0040194 0040195 PUBLIC ipaddr_t ip_netmask(nettype)0040196 nettype_t nettype;ip_netmask()
ip_netmask() returns a nettype's associated subnet mask.
For a class A network, the subnet mask is 255.000.000.000 (0xff000000);
for a class B network, the subnet mask is 255.255.000.000 (0xffff0000);
for a class C network, the subnet mask is 255.255.255.000 (0xffffff00);
for a zero network type (0.xx.xx.xx), the subnet mask is (0x00000000).
Note that the returned subnet mask is in network format.
ip_netmask() returns a nettype's associated subnet mask.
For a class A network, the subnet mask is 255.000.000.000 (0xff000000);
for a class B network, the subnet mask is 255.255.000.000 (0xffff0000);
for a class C network, the subnet mask is 255.255.255.000 (0xffffff00);
for a zero network type (0.xx.xx.xx), the subnet mask is (0x00000000).
Note that the returned subnet mask is in network format.
0040197 {0040198 switch(nettype)0040199 {0040200 case IPNT_ZERO: return HTONL(0x00000000);0040201 case IPNT_CLASS_A:0040202 case IPNT_LOCAL: return HTONL(0xff000000);0040203 case IPNT_CLASS_B: return HTONL(0xffff0000);0040204 case IPNT_CLASS_C: return HTONL(0xffffff00);0040205 default: return HTONL(0xffffffff);0040206 }0040207 }0040208 0040209 #if 00040210 PUBLIC char *ip_nettoa(nettype)0040211 nettype_t nettype;0040212 {0040213 switch(nettype)0040214 {0040215 case IPNT_ZERO: return "zero";0040216 case IPNT_CLASS_A: return "class A";0040217 case IPNT_LOCAL: return "local";0040218 case IPNT_CLASS_B: return "class B";0040219 case IPNT_CLASS_C: return "class C";0040220 case IPNT_CLASS_D: return "class D";0040221 case IPNT_CLASS_E: return "class E";0040222 case IPNT_MARTIAN: return "martian";0040223 case IPNT_BROADCAST: return "broadcast";0040224 default: return "<unknown>";0040225 }0040226 }0040227 #endif0040228 0040229 /*0040230 * $PchId: ip_lib.c,v 1.6 1996/12/17 07:59:36 philip Exp $0040231 */